
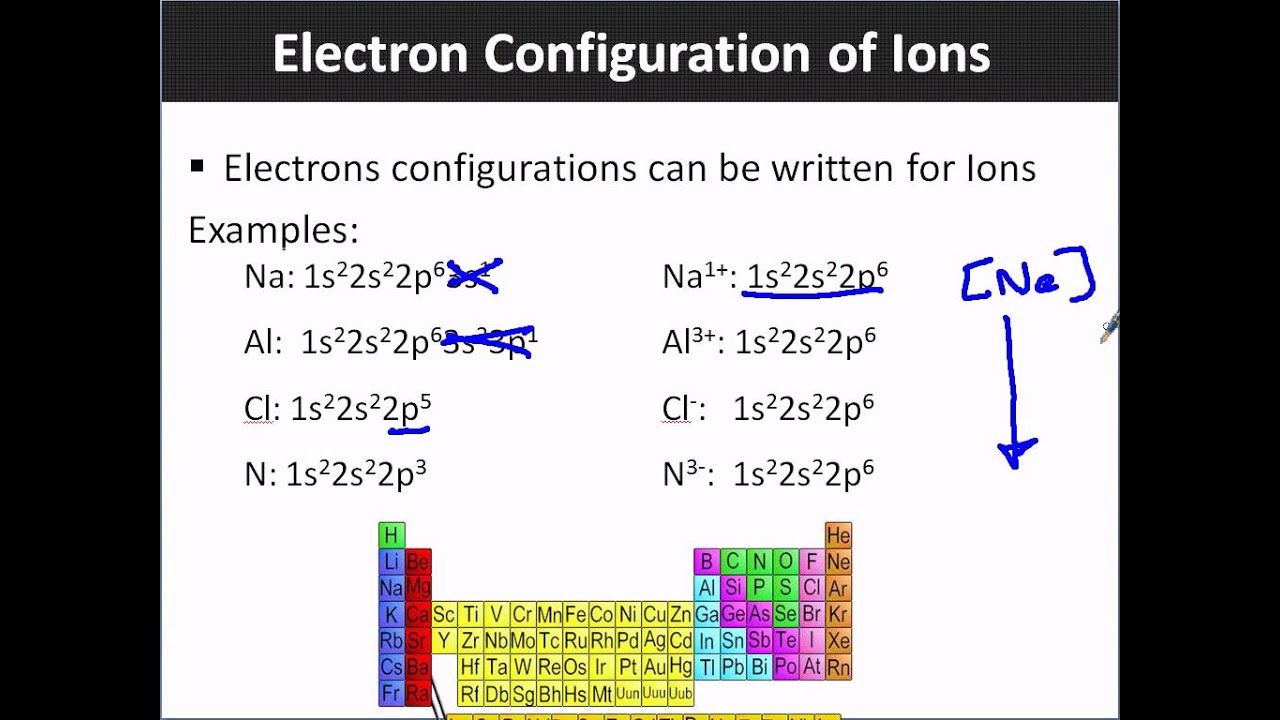

Thus, the two electrons in the carbon 2 p orbitals have identical n, l, and m s quantum numbers and differ in their m l quantum number (in accord with the Pauli exclusion principle). The orbitals are filled as described by Hund’s rule: the lowest-energy configuration for an atom with electrons within a set of degenerate orbitals is that having the maximum number of unpaired electrons. We now have a choice of filling one of the 2 p orbitals and pairing the electrons or of leaving the electrons unpaired in two different, but degenerate, p orbitals. The remaining two electrons occupy the 2 p subshell. Four of them fill the 1 s and 2 s orbitals. If you want to also include sub-levels, then the configuration. When drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same subshell that we are filling.Ĭarbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. In a summary, the electron configuration is (just considering the main energy levels) 2-8188. There are three degenerate 2 p orbitals ( m l = −1, 0, +1) and the electron can occupy any one of these p orbitals. The electron configuration of strontium ion (Sr 2+) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6. Because any s subshell can contain only two electrons, the fifth electron must occupy the next energy level, which will be a 2 p orbital. The strontium atom donates two electrons of the last shell to form bonds and turns into a strontium ion (Sr 2+ ). Electron Configuration of the elements Bohrium, Rn7s25f146d Nobelium Boron, He2s22p Oganesson Bromine, Ar4s23d104p Osmium Cadmium, Kr5s24d. The n = 1 shell is filled with two electrons and three electrons will occupy the n = 2 shell. Atomic number The number of protons in an atom. These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: sharp (s), principal (p), diffuse (d), and fundamental (f). The fourth electron fills the remaining space in the 2 s orbital.Īn atom of boron (atomic number 5) contains five electrons. Elements are organised into blocks by the orbital type in which the outer electrons are found. Tin has a ground state electron configuration of 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p2 and can form covalent tin (II) compounds with its two unpaired p-electrons. Thus, the electron configuration and orbital diagram of lithium are:Īn atom of the alkaline earth metal beryllium, with an atomic number of 4, contains four protons in the nucleus and four electrons surrounding the nucleus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
